Have you ever faced the disappointment of discovering spoiled vegetables in your storage area, especially when prepping for a big service? Keeping your produce fresh is more than a task; it’s an art that every chef should master. In the fast-paced world of restaurant kitchens, understanding how to properly store your fruits and vegetables can make a significant difference in the quality of your dishes and your bottom line. We’re here to help.
Let’s get into some practical, no-nonsense tips for storing your produce. These strategies are designed to keep your ingredients at their peak for as long as possible, ensuring that every dish you serve is as fresh as can be.
Understanding Ethylene Producers and Sensitive Produce
Ethylene is a natural gas that some fruits and vegetables emit, accelerating ripening and, unfortunately, spoilage. Apples, bananas, and tomatoes are high ethylene producers, while leafy greens and potatoes are ethylene-sensitive. Keep them separated to avoid premature spoilage. Think of your storage space as a map, and strategically place your produce according to their ethylene characteristics.
High Ethylene Producers: Apples, avocados, bananas, peaches, pears, plums, and tomatoes produce high levels of ethylene. Store these items away from ethylene-sensitive produce to prevent hastening their ripening process.
Ethylene Sensitive: Leafy greens, broccoli, carrots, cucumbers, eggplants, potatoes, and watermelons are sensitive to ethylene. These should be stored separately from high ethylene producers to avoid premature spoilage.

Optimal Temperature and Humidity Zones
Different produce items thrive in different environments. Most vegetables prefer a cool, humid environment (around 45-50°F and 95% humidity), while fruits generally do best in a slightly warmer setting (about 50-60°F with 85-90% humidity). Investing in storage units that allow you to control temperature and humidity can drastically extend the life of your produce.
Leafy Greens: Store unwashed leafy greens at temperatures around 40°F. The shelf life of lettuce varies with its variety’s resilience. Green leaf and romaine last up to a week, whereas loose leaf, along with delicate Bibb and butter lettuces, spoil more quickly.
Root Vegetables: Carrots, turnips, and beets prefer cooler temperatures (32-40°F) and high humidity. When purchasing carrots, beets, or turnips with their greens attached, detach the greens to prevent them from drawing moisture from the root, helping the roots stay fresh longer. Store the roots in sealed zip-top bags or airtight containers in the fridge, and they’ll remain fresh for several weeks. Don’t discard the greens; they’re tasty in soups or stir-fries. Keep them separately like any leafy greens, and they’ll last about a week.
Tomatoes: Keep tomatoes at room temperature away from direct sunlight until they ripen. Once ripe, they can be moved to the refrigerator but should be brought back to room temperature before serving to enhance their flavor.
Eggplants: Store at room temperature if using within two days or in the crisper drawer of your refrigerator for longer storage. Avoid cold temperatures, which can damage their texture.
Potatoes & Sweet Potatoes: Store them in a cool, dark, and somewhat humid environment with good air flow. Both starchy varieties like russets and waxy types like Yukon Golds will last for several weeks if kept in a cool, dark location like an air-conditioned pantry, ensuring they are not near heat-producing appliances.
Bananas: Store bananas at room temperature, away from direct sunlight and heat to allow them to ripen evenly. Once they reach your desired ripeness, you can slow down further ripening by placing them in the refrigerator. The peel may turn brown, but the fruit inside will stay fresher for longer.
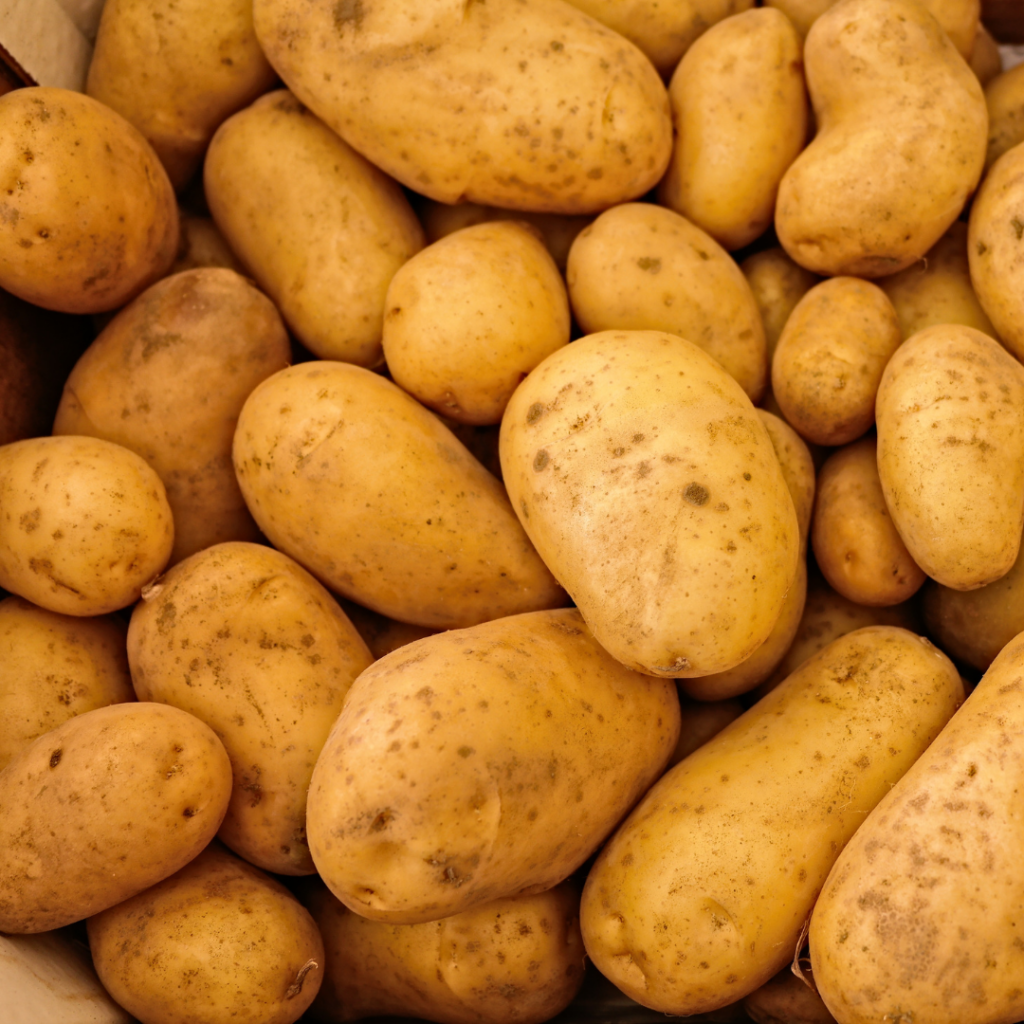
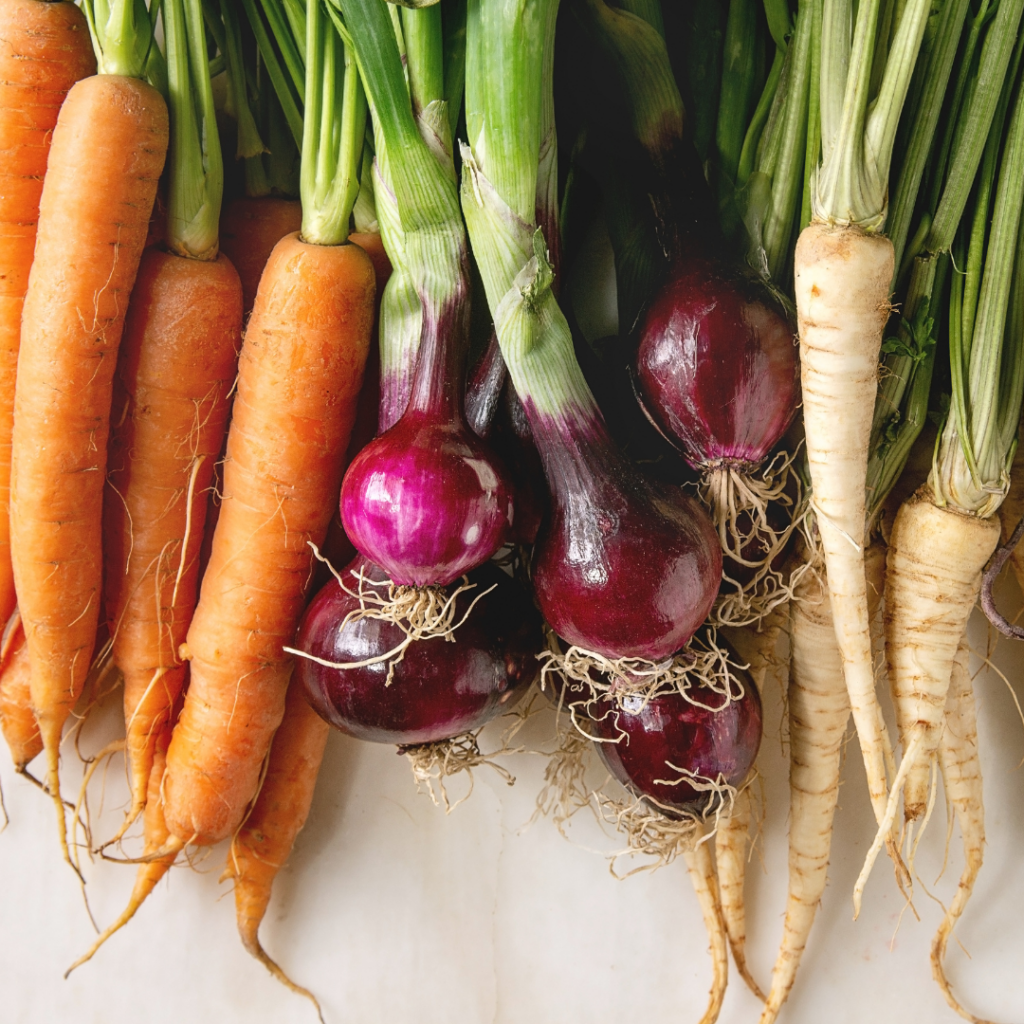



Proper Air Circulation is Key
Avoid packing your produce too tightly. Good air circulation is crucial to preventing mold growth and ensuring even temperature distribution. This might mean rethinking how you organize your walk-in cooler or storage shelves, but the effort will pay off in reduced waste and better-quality ingredients.
Mushrooms: Store in a paper bag in the refrigerator to allow air circulation. Plastic can trap moisture, leading to slimy mushrooms.
Berries: Keep berries in their original container in the refrigerator for proper air circulation. Avoid washing until right before use to prevent mold growth.
Citrus Fruits: Store lemons, limes, oranges, and grapefruits in a mesh bag or in the crisper drawer of your refrigerator. This allows for air flow and prevents them from absorbing flavors from other foods.



Dry vs Damp Storage
Some items, like onions and garlic, prefer a dry, well-ventilated space away from the cooler. On the other hand, leafy greens do best when slightly damp. Wrapping these in a damp cloth or storing in containers with a small amount of water can keep them crisp and fresh for longer.
Onions and Garlic: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, never in a plastic bag or airtight container. They prefer darkness and can last for several months when stored properly. Avoid storing near potatoes, which can emit moisture and gases that can cause onions to spoil more quickly. Don’t worry if your alliums start sprouting green shoots; both the bulbs and the shoots are edible.
Herbs: Soft herbs like cilantro and basil enjoy a damp environment. Trim the stems, place them in a glass of water, and cover loosely with a plastic bag to create a mini greenhouse effect. Hard herbs like rosemary and thyme can be wrapped in a damp paper towel and stored in a container in the refrigerator.


Regularly Rotate Your Stock
First in, first out (FIFO) isn’t just a catchy acronym; it’s a principle that should govern how you manage your inventory, but you know that. Regularly rotating your stock ensures that older produce gets used before it spoils, reducing waste and saving money.
Invest in Quality Storage Containers
Not all storage containers are created equal. Invest in high-quality, food-safe containers that are designed for produce storage. Look for features like built-in ventilation or the ability to regulate humidity. These containers can be a game-changer for extending the shelf life of your fruits and vegetables.
Use moisture-control mats when you can. Place these mats at the bottom of shelves or bins where you store produce. They help maintain optimal moisture levels and prevent the direct contact of produce with cold surfaces, reducing spoilage.
Be Mindful of Cross-Contamination
Always be aware of the potential for cross-contamination between produce and other foods, especially raw meats. Always store fruits and vegetables above raw meats, poultry, and seafood to prevent any drips or contamination.
At What Chefs Want, we understand that managing a kitchen’s inventory, especially the produce, can be challenging. But with our fresh produce delivery, the right knowledge and tools, it’s possible to significantly reduce waste, save money, and ensure that your dishes are always made with the freshest ingredients possible. Our produce experts are always here to provide guidance, answer your questions, and help you select the best products for your needs. Don’t hesitate to reach out to us for personalized advice on how to keep your fruits and vegetables in top condition. Let us help you make your kitchen operations smoother, one fresh ingredient at a time.